What makes Singapore a leader in smart city innovations?
It’s the power of IoT!
As one of the world’s most advanced cities, Singapore is implementing IoT technology across a variety of sectors, creating an interconnected, efficient, and sustainable urban environment.
Here are the TOP 7 examples of how Singapore transformed from a city-state to a smart city using IoT.
1. Smart Water Management: Every Drop Counts
Singapore’s forward-thinking approach to water conservation is nothing short of revolutionary. The city has deployed smart water IoT meters that keep an eye on water usage in real-time. These meters can detect leaks and inefficiencies almost instantly, ensuring that not a single drop goes to waste.
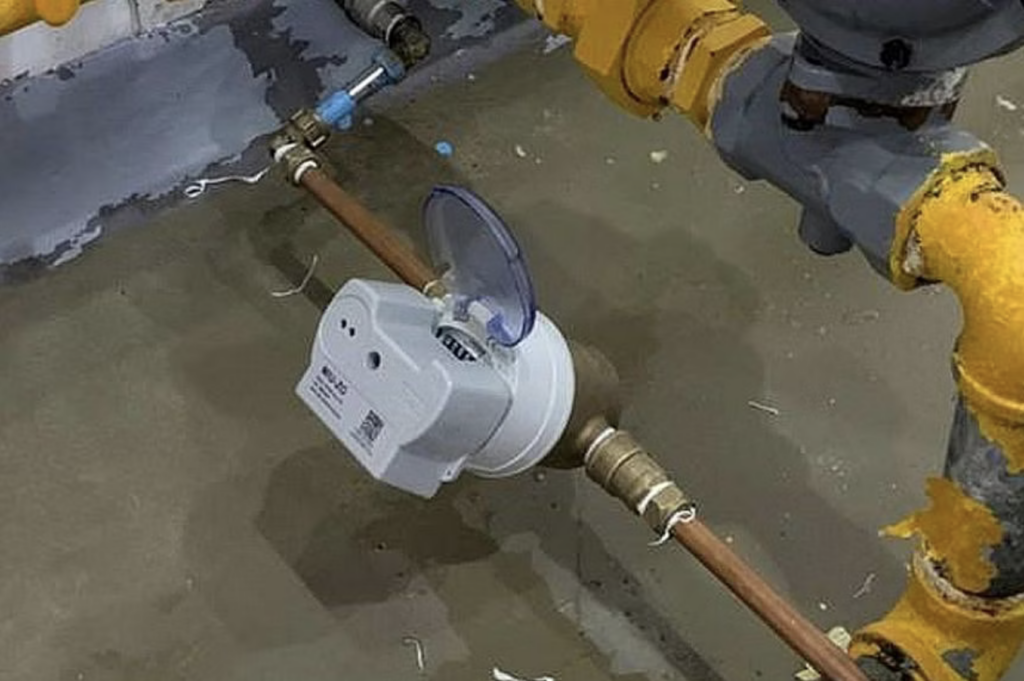

The smart meters are part of Singapore’s broader water management strategy aimed at sustainability. By monitoring water usage closely, the system helps identify potential leaks and encourages residents to adopt water-saving habits. During pilot trials, households using smart meters saved an average of 5% of their water consumption due to early leak detection and increased awareness of usage patterns. (2)
2. Green Building Monitoring: Pioneering Sustainability
The Green Building Masterplan in Singapore leverages IoT technology to push the boundaries of energy efficiency. Sensors are strategically placed in buildings to manage lighting and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems. These sensors collect data in real time, making automatic adjustments to optimize energy consumption. The result? Significant energy savings and a step closer to the city’s ambitious sustainability goals. (3)
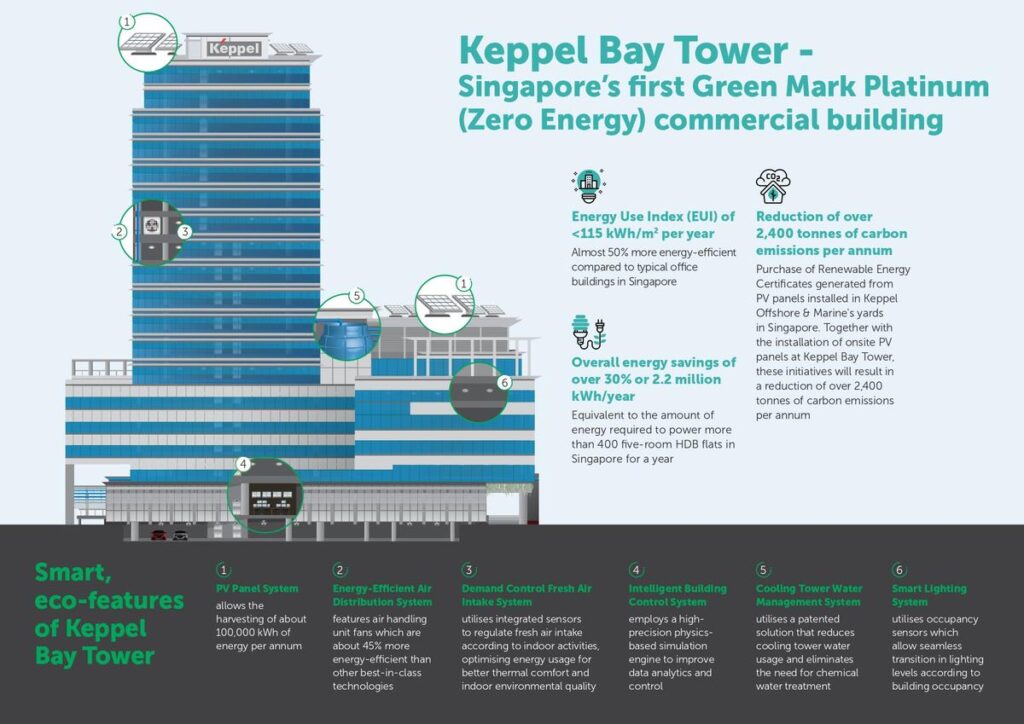
An example is Keppel Bay Tower in Singapore. This 20-year-old building was upgrated to enhance its energy efficiency, making it the first commercial building in the city-state to receive the Green Mark Platinum (Zero Energy) certification. This milestone was achieved by implementing innovative solutions such as smart lighting, onsite solar power generation, and advanced systems for monitoring the building’s cooling processes. (2)
The plan aims for 80% of buildings by gross floor area to be green by 2030, with a focus on achieving super-low energy standards. This initiative is part of Singapore’s broader sustainability goals under the Singapore Green Plan 2030 (3), which emphasizes the importance of energy-efficient buildings in reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable development.
3. Smart Parking Solutions: Ending the Hunt for Parking
Anyone who’s driven in an urban area knows the frustration of finding a parking spot. In bustling areas like Marina Bay, IoT sensors provide real-time information on parking availability. Just like when using our ParkingAround app, drivers are guided to open spots through mobile apps, reducing the time spent searching and cutting down on emissions. It’s a win-win for both convenience and the environment.
Meanwhile, Singapore’s Mass Rapid Transit (SMRT) system employs IoT to ensure operational efficiency and reliability. Sensors on trains monitor conditions and passenger loads, offering real-time data that helps manage service effectively. This integration ensures that the SMRT remains one of the most efficient and dependable public transport systems globally. (7)
4. Predictive Healthcare: A New Era of Health Monitoring
Imagine a healthcare system that knows you’re unwell before you do. Singapore’s healthcare incorporates IoT wearables to monitor patients from the comfort of their homes. These wearables track vital statistics and send data to healthcare providers in real time, allowing for early detection of health issues. By leveraging IoT technology, healthcare providers can optimize their resources, potentially reducing the need for additional healthcare personnel. This is particularly important as Singapore faces a growing elderly population and increasing healthcare demands

5. Efficient Waste Management: Smarter, Cleaner Cities
IoT-enabled waste bins notify collection services when they’re full, allowing for optimized collection routes and reduced fuel consumption. This not only keeps the city cleaner but also cuts down on operational costs and environmental impact. It’s part of Singapore’s broader strategy to maintain cleanliness and efficiency across its urban landscape. (8)
6. Urban Farming with IoT: Growing the Future
Food security is a critical concern for any city, and Singapore is tackling this issue head-on with IoT-powered urban farming. The use of IoT in urban farming aligns with Singapore’s “30 by 30” strategy, which aims to locally produce 30% of the country’s nutritional needs by 2030. (6) Sensors monitor environmental conditions like humidity, temperature, and soil quality, ensuring optimal growth conditions for crops.
Many urban farms in Singapore, including AbyFarm, employ soil-less farming techniques such as hydroponics and aeroponics. (9) These methods are particularly suited for urban environments and are enhanced by IoT for better resource management, leading to higher yields and reduced resource consumption.
7. Air Quality Monitoring: Breathing Easy
Air quality is a crucial factor in public health, and Singapore is using IoT to keep its residents informed and safe. Sensors placed throughout the city monitor air quality parameters such as particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon dioxide (CO2), and other contaminants, providing valuable data to both the government and the public. (10) This information helps residents make informed decisions about outdoor activities and raises awareness about environmental health. The real-time data is often displayed publicly, either through mobile apps or large screens in public areas. This raises awareness about environmental health and encourages residents to take steps to improve air quality
The Bigger Picture: Singapore’s Commitment to Innovation
Singapore’s comprehensive implementation of IoT technologies showcases the city’s unwavering commitment to innovation and sustainability. By integrating these smart solutions across various sectors, Singapore provides a model for what future smart cities can achieve.
From smart water management to efficient waste collection and beyond, the city’s innovations highlight the incredible potential of IoT to create more connected, efficient, and sustainable urban environments. Singapore’s smart solutions offer a blueprint for how IoT can be leveraged for the greater good.
Sources:
- (1) First 300,000 smart water meters in S’pore to be installed by SP Services from 2022
- (2) Smart Water Meter
- (3) Green Building Masterplans
- (4) Keppel Bay Tower: Singapore’s First Green Mark Platinum (Zero Energy) Commercial Building
- (5) Establishing a Sustainable Future One Building at a Time
- (6) A City of Green Possibilities
- (7) Solving Challenges, Empowering Efficiency: IoT in Rail and Public Transportation
- (8) Smart Waste Management in Singapore
- (9) IoT sensors enable urban farming in Singapore
- (10) Air Quality Monitoring

Leave a Reply